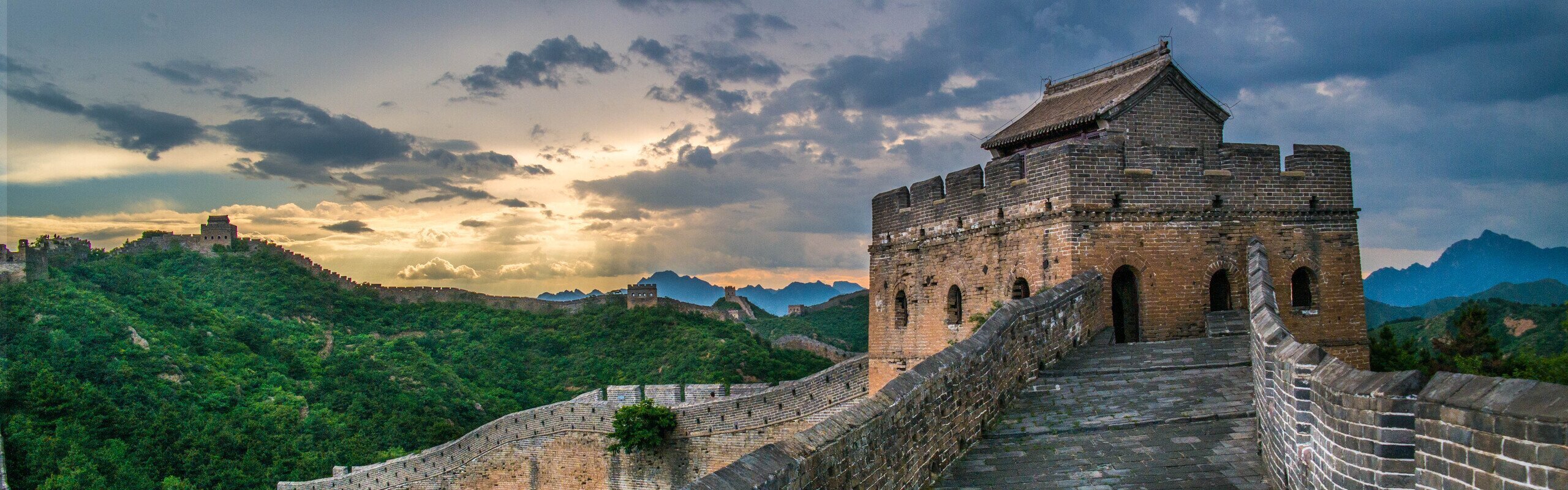
The Great Wall easily required the greatest human effort of any ancient construction! 100 million tonnes of bricks, stone, and soil were transported and assembled by millions of soldiers, peasants, prisoners, and animals using basic rope, wood, and basket systems on remote terrain ranging from parched desert to steep mountain ridges.
Read on and find out more about the labor force, terrain, materials, and technology used — answers you may never have thought of…
Where the Great Wall Was Built — 2 terrains
 The Great Wall along mountain ridges
The Great Wall along mountain ridgesOver the Great Wall's thousands of miles the terrain changes from desert to riverside, from mountains to plains. The Great Wall designers took advantage of the terrain, and built at strategic places to repel invaders most effectively.
From the Great Wall relics we can see that the wall is either built along mountain ridges, across mountain passes, or across key transportation areas on flat land.
Watchtowers and beacon towers were built high for observation and communication by signal fire.
On the plains and deserts, designers made use of rivers (and their cliffs) as natural barriers. This not only controlled strategic places, but also saved labor and materials.
4 Great Wall Building Materials — stone, soil, sand, brick
 Jiayuguan's Great Wall section in west China was mainly built with dusty loess soil.
Jiayuguan's Great Wall section in west China was mainly built with dusty loess soil.Most of the (restored) Great Wall sections we see today were built with bricks, and cut stone blocks/slabs. Where bricks and blocks weren't available, tamped earth, uncut stones, wood, and even reeds were used as local materials.
Wood was used for forts and as an auxiliary material. Where local timber wasn't enough, they had it delivered in.
Stone Great Wall Sections
In mountain areas, workers quarried stone to build the Great Wall. Using the mountains themselves as footings, the outer layer of the Great Wall was built with stone blocks (and bricks), and filled with uncut stone and anything else available (like earth and dead workers).
Soil Great Wall Sections
On the plains Great Wall workers made use of local soil (sand, loess, etc.) and rammed it into compact layers. Jiayuguan's Great Wall section in west China was mainly built with dusty loess soil — "the most erodible soil on the planet". It's amazing that sections 2,000 years old still remain mostly intact!
Sand (and Reed/Willow) Great Wall Sections
 The Great Wall at Mutianyu was built with bricks.
The Great Wall at Mutianyu was built with bricks.Sand doesn't stick together, so how could a wall be built with sand? Sand was used as a fill material between reed and willow layers.
West China around Dunhuang is desert. Innovative builders there made use of reeds and willow brought in from rivers and oases to build a strong wall. Jade Gate Pass (Yumenguan) Great Wall Fort was built with 20-cm layers of sand and reed, an impressive 9 meters high.
Brick Great Wall Sections
The Ming Dynasty Great Wall was mostly built with bricks. To build a strong wall with bricks, they used lime mortar. Workers built brick and cement factories with local materials near the wall.
- 1-Day Beijing Layover Tour
- 1-Day Jiankou to Mutianyu Great Wall Hiking Tour
- 5-Day Badaling to Huangyaguan Great Wall Hiking Tour

Transporting 100,000,000 Tonnes — by hand, rope, cart … goat?
The Great Wall over the ages used around 100,000,000 tonnes of stone, bricks, and mud. According to history and legend, there were three ways to get the materials up the mountains and across the plains...
Carried by Hand — the usual way
Workers carried most of the stones and bricks up the mountains on their shoulders or backs. Bamboo baskets were used for soil, loose stone, and lime mortar.
Human chains were also used to pass the blocks and baskets up. Lining up on narrow mountain paths was more efficient than trudging back and forth.
Primitive Technology — wheel barrows and ropes
On mountains with flat enough paths, one-wheel barrows were used. Basket and pulley systems were used over deep valleys, and materials were also pulled to the top of the Great Wall on ropes.
Animal Use — doubtless fact and doubtful legend
Doubtless horses/oxen and carts were used in the flatter areas for transporting materials, and camels were used in the deserts for long distances.
There is a doubtful legend that when Badaling's Great Wall section was built on the steep mountains, workers used goats to deliver the materials. Goats are renowned for being good at "climbing", so it's said people tied bricks on goats' horns and made them carry them up the steep mountains.
Great Wall Laborers' Laments
During the construction of the Great Wall, millions of people died. Many poets expressed their resentment with poems, along the lines of:
'Every brick, every stone,
and every inch of mud
are filled with Chinese people's
bones and sweat and blood.'
- 1-Day Beijing Highlights Private Tour
- 3-Day Jiankou to Jinshanling Great Wall Hiking Discovery Tour
- 2-Day Jiankou Wild Great Wall Camping Tour
You Should Appreciate Great Wall Construction in Person

If you are interested in a Great Wall tour to discover more about this impressive construction, see the recommended tours below for inspiration:
- The most beautiful hiking route: 1-Day Simatai-West-to-Jinshanling Great Wall Hiking Tour
- Hike two wild, two restored sections: 3-Day Jiankou to Jinshanling Great Wall Hiking Tour
- The comprehensive classic Beijing itinerary: Private 4-Day Emperor's Tour of Beijing with Mutianyu Great Wall Hiking
Not interested in the above tours? You can tell us your interests and requirements, and China Highlights will create a Great Wall tour to your specification.
Learn More about the Great Wall
- How Long It Took to Build the Great Wall of China?
- Why the Watchtowers Were Built on the Great Wall?
- What Was the Great Wall of China Made of?
- How Was the Great Wall Defended?
- Why the Great Wall WAS, and STILL IS, So Important?
- Why the Great Wall Was Built?
- What to Pack for Great Wall Trips?
- Current Situation of the Great Wall of China
- Great Wall Threat and Protection
- Over 300 Famous People Have Visited the Great Wall


 (10,000+ reviews)
(10,000+ reviews)